

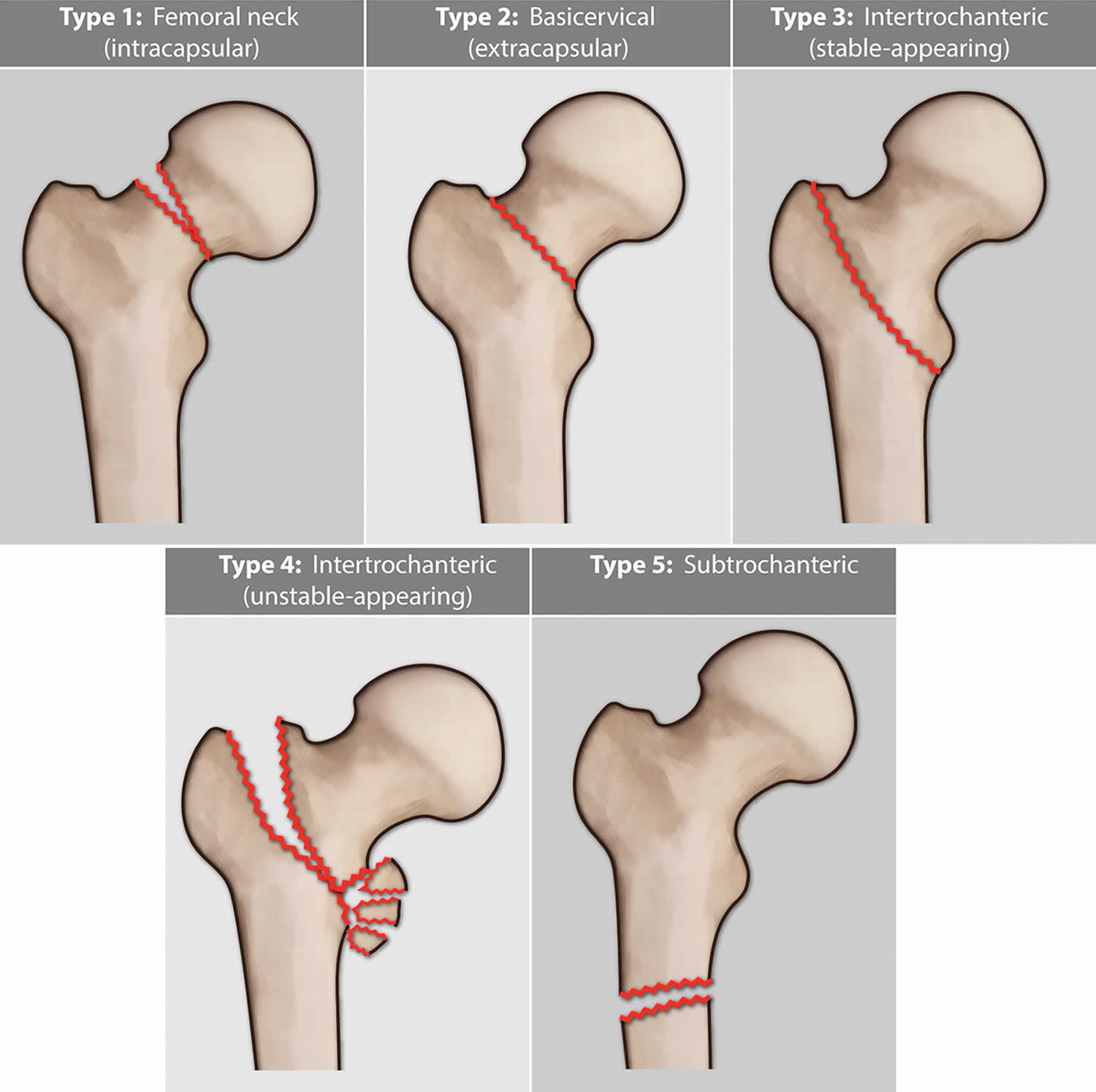
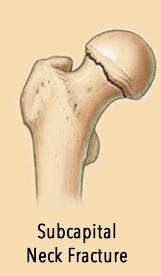
Kim et al studied the timing at which patients underwent the internal fixation. Internal fixation Timing of internal fixation Surgical treatments mainly include internal fixation and joint replacement (especially hemiarthroplasty or total arthroplasty), which are systematically reviewed and summarized in the following sections. Ĭompared to the surgical treatments, conservative treatments are associated with much more mobility restrictions, bed-related complications, family care, etc, which increase the total cost, morbidity, and mortality. The 3D reconstruction of hip joint can be used to reconstruct the exact status of fracture, so as to assist the surgeons to judge the fracture type according to the Garden classification and provide scientific basis for the development of treatment plan and assessment of prognosis. With the advantages of intuitive and multiple-angle vision, 3D reconstruction can display the anatomical shape of the femoral neck and is superior to X-ray in diagnosis and displacement judgment of fracture. In addition, compared with the use of Garden classification alone, it is more effective to combine the three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of hip joint with Garden classification to fully evaluate the NDFNFs. Since NDFNFs also involve fracture lines, the CT scan shows the pattern of the fracture more clearly for treatment plan. Moreover, Cserhati et al also revealed that the complication rate, especially the osteonecrosis of femoral head (ONFH), after conservative treatment was 18.9%, which was much higher than that of surgical treatment (3.2%). Therein, the incidence of complications in the conventional treatment group was as high as 30-40%. In a recent retrospective study, Rzesacz et al revealed that conservative treatments were associated with a higher complication rate as compared to surgical treatments. The complication rate of type II fractures is 1.5 times higher than that of type I fractures. Garden type I fractures can be treated conservatively, but misdiagnosis and osteoporosis may lead to secondary displacement. Conservative treatmentīoth Garden type I and II fractures are NDFNFs. Furthermore, after excluding the case reports, case series, review articles, conference abstracts, expert opinions and incomplete data sets, a total of 23 full-text articles were ultimately included in the final review. Hemiarthroplasty is also an alternative for old patients with higher risks of displacement and avascular necrosis of the femoral head.Ī total of 149 articles were included in the retrieval process, and the records after duplicate removal were 87. Surgical treatments may be a better option because the implants provide additional stability and allow early exercise and ambulation. The non-displaced femoral neck fractures are relatively stable but carry a risk of secondary displacement. Specific surgical strategies and implant selection were important for the patient’s functional recovery. Otherwise, surgical treatment was a better choice. Patients who were unable to tolerate the operation and anesthesia could be treated conservatively. Four major medical databases and a combination of the search terms of “femoral neck fractures”, “nondisplaced”, “undisplaced”, “non-displaced”, “un-displaced”, “aged”, “the elderly”, and “geriatric” were used to search the literature relevant to the topic of the review. Reviewed was the literature on non-displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. We also discussed the surgical and non-surgical treatments and selection of implants.
This paper aimed to review the databases on non-displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
